TFNR - Properties of the Structures of Information
Different kinds of Structures have different properties. In general, we can say that all the Physical Structures of Information have causal, spatial and temporal extension. Other properties are related to the shape of the structure (the form in the space), to its dynamics (the form in the time), to the way in which it can interact with other structures. Many other properties derive from the way in which the single structure is aggregated with other forms. In other words, the properties of the structures imply the properties of the more complex aggregates to which they take part, and the emerging properties of the aggregates imply the properties of the structures that compose the aggregates themselves. The elementary and the complex co-evolve influencing each other.
Physical Structures have causal, spatial and temporal extension:
- causal extension: Structures are derived centers of action, able to express action, to produce events, to express derived forces in sub processes of formation that from the Force lead to the Physical Forms, composed by the same Structures. They are one of the steps of the main causal chain (Force-Action- Information-Form), representing, as stated, the structured aspect of Information;
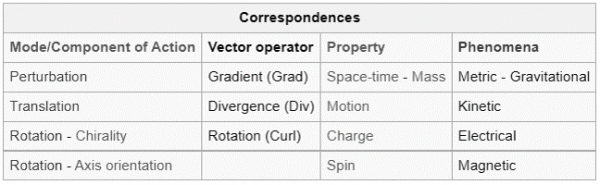
- spatial extension: potentially any vortex structure has an infinite spatial extension, the limits being only determined by the decreasing, moving away from the “center” of the structure, of the Action forming the structure in its modes of expression (Perturbation, Translation, Rotation, with their physical quantity counterparts: mass, motion, charge and spin). The same potentially infinite spatial extension, even with a slightly different configuration, characterizes wave structures, always produces by the dynamics of vortex structures. In general, Structures have an extremely huge extension compared with the dimensions of the tiny fluctuation of space time field that characterize the factory of Reality at the Planck scale;
- temporal extension: it can span from the smaller period that can be associated to the Planck time to the supposed infinite lifetime of a stable particle as proton. In general, the lifetime of a Structure is influenced by its shape, by the composition for composite structures, by the velocity of its movement, the energetic environment in which it stays and moves (the local state of the Field: the casual fluctuations of the Field itself and the quantum fluctuations of the same structure), not considering the interactions of the structure with other structures and the derived forces expressed by them.
Each type of Structure of Information has / shows different Properties (attributes, characteristics, ways of expressions, qualities and quantities of Entities, Events, Relations, Processes, Phenomena. Examples of fundamental properties: Causality, Variationality, Spatiality, Temporality, Existence, Essence / Form, Extension and Size, Capacity, Behavior).
The properties of the Structures of Information determine their Dynamics and the Phenomena in which they participate (Phenomena are the answer to the questions "what happens?" and "how happens?"). They are Events organized by Relations. They are what has the property that we call Essence / Form added to the fundamental property of Entities (that produce Events), that we call Existence).
On the physical side of Reality, the fundamental Properties of the Structures of Information, are Space-time extension, Mass, Motion, Charge and Spin. They represent "dynamical states" the Elementary Field itself, organization of the Elementary Action, in its three modes of expression: Perturbation, Translation and Rotation (in its two submodes: Chirality and Axis Orientation).
Properties of Physical Structures of Information
Each type of Physical Structure of Information has / shows different Properties (attributes, characteristics, ways of expressions, qualities and quantities of Entities, Events, Relations, Processes, Phenomena. Examples of fundamental properties: Causality, Variationality, Spatiality, Temporality, Existence, Essence / Form, Extension and Size, Capacity, Behavior).
The properties of the Structures of Information determine their Dynamics and the Physical Phenomena in which they participate (Phenomena are the answer to the questions "what happens?" and "how happens?"). They are Physical Events organized by Physical Relations. They are what has the property that we call Essence / Form added to the fundamental property of Physical Entities (that produce Physical Events), that we call Physical Existence).
On the physical side of Reality, the fundamental Properties of the Physical Structures of Information, are Space-time extension, Mass, Motion, Charge and Spin. They represent "dynamical states" the Elementary Field itself, organization of the Elementary Action, in its three modes of expression: Perturbation, Translation and Rotation (in its two submodes: Chirality and Axis Orientation).
Links to the tables of contents of TFNR Paper