TFNR - Properties of the Structures of Information
Each type of Structure of Information has / shows different Properties (attributes, characteristics, ways of expressions, qualities and quantities of Entities, Events, Relations, Processes, Phenomena. Examples of fundamental properties: Causality, Variationality, Spatiality, Temporality, Existence, Essence / Form, Extension and Size, Capacity, Behavior).
The properties of the Structures of Information determine their Dynamics and the Phenomena in which they participate (Phenomena are the answer to the questions "what happens?" and "how happens?"). They are Events organized by Relations. They are what has the property that we call Essence / Form added to the fundamental property of Entities (that produce Events), that we call Existence).
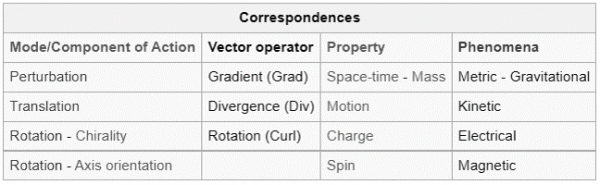
On the physical side of Reality, the fundamental Properties of the Structures of Information, are Space-time extension, Mass, Motion, Charge and Spin. They represent "dynamical states" the Elementary Field itself, organization of the Elementary Action, in its three modes of expression: Perturbation, Translation and Rotation (in its two submodes: Chirality and Axis Orientation).
Properties of Physical Structures of Information
Each type of Physical Structure of Information has / shows different Properties (attributes, characteristics, ways of expressions, qualities and quantities of Entities, Events, Relations, Processes, Phenomena. Examples of fundamental properties: Causality, Variationality, Spatiality, Temporality, Existence, Essence / Form, Extension and Size, Capacity, Behavior).
The properties of the Structures of Information determine their Dynamics and the Physical Phenomena in which they participate (Phenomena are the answer to the questions "what happens?" and "how happens?"). They are Physical Events organized by Physical Relations. They are what has the property that we call Essence / Form added to the fundamental property of Physical Entities (that produce Physical Events), that we call Physical Existence).
On the physical side of Reality, the fundamental Properties of the Physical Structures of Information, are Space-time extension, Mass, Motion, Charge and Spin. They represent "dynamical states" the Elementary Field itself, organization of the Elementary Action, in its three modes of expression: Perturbation, Translation and Rotation (in its two submodes: Chirality and Axis Orientation).
Links to the tables of contents of TFNR Paper